7 Components of an Effective Safety Meeting Agenda
Safety meetings are a valuable tool for keeping employees safe. Learn how to structure effective and engaging meeting agendas to foster your company’s safety culture.

It’s 9:05 on a Monday morning and your sales team has slowly filtered into a conference room. Everyone is sipping coffee, a few people look half-asleep, and you’re about to dive into a riveting PowerPoint presentation on business travel safety. Not exactly a recipe for a productive meeting, is it?
Regular safety meetings are an integral part of a positive safety culture. But holding meetings isn’t enough—you need your team’s interest and engagement if the information sharing is going to pay off.
To maximize your safety meetings, plan your agenda carefully. More than just a list of key points on a slide, consider your objectives and audience thoughtfully and deliver content that promotes participation in workplace safety initiatives.
Read on to learn about structuring safety meeting agendas to maximize engagement and knowledge retention.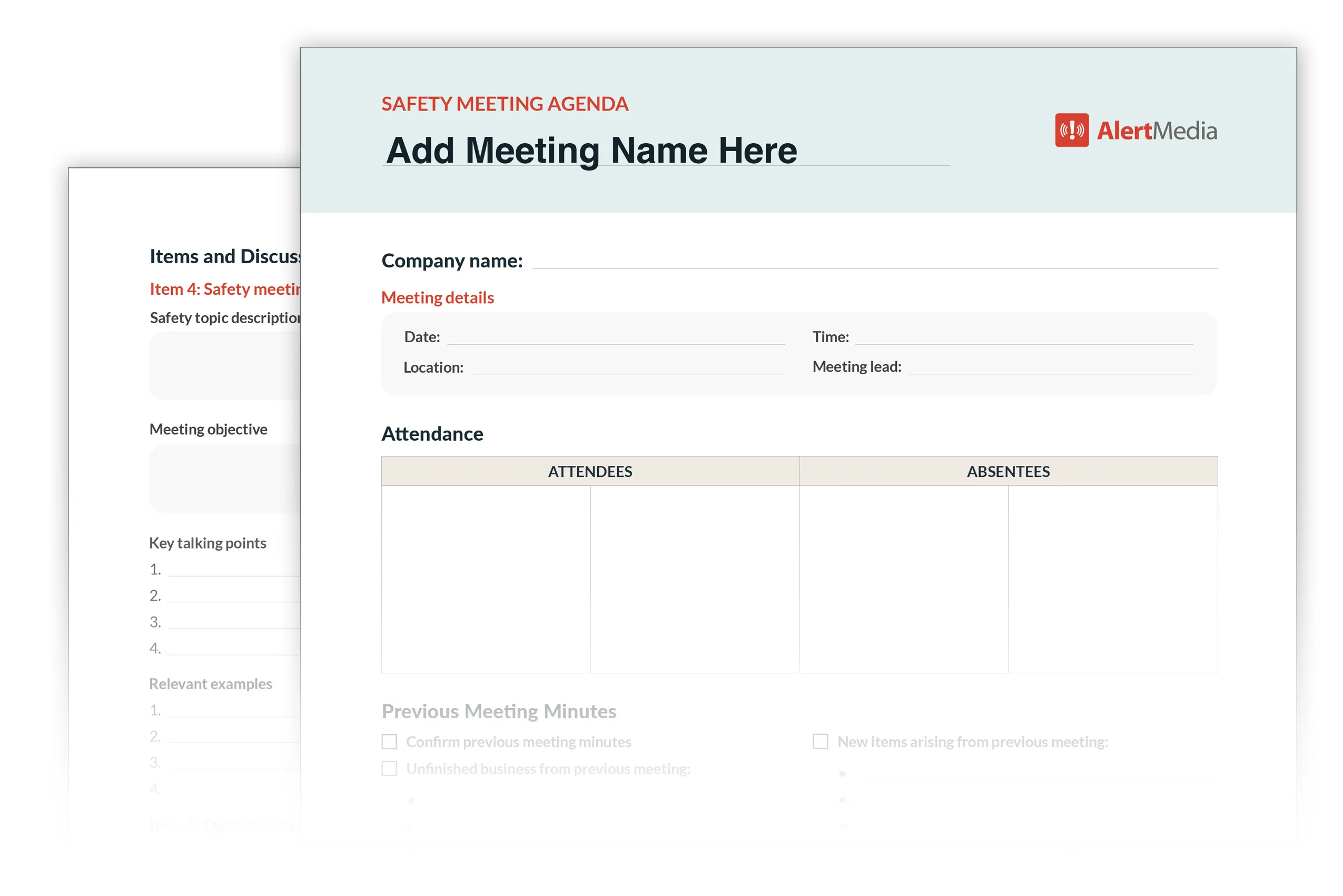
Preview of the Safety Meeting Agenda template in the AlertMedia toolkit
Safety Meeting Toolkit
Establish Safety Meeting Objectives
The main key to an effective safety meeting agenda is understanding your goals. Everyone in your organization has a full plate of responsibilities. When you ask them to take time out of their day, you need to make it count for them individually and the company as a whole.
What are your primary objectives for a single meeting or a series of safety meetings?
- Training and education: Safety meetings are a good opportunity to supplement in-depth education programs. Use meetings to introduce new concepts, supplement employee training, or as a refresher.
- Compliance: Many businesses have to provide regular instruction on OSHA safety topics. Covering and documenting relevant topics and safety regulations during meetings helps to keep your organization compliant with government and industry standards.
- Facilitating communication: Meetings are more than a chance to shove information at employees and move on. Field questions, promote open discussion, and give your team the opportunity to engage in two-way safety communication.
- Team-building: Employee safety isn’t just about systems and personal protective equipment (PPE)—it’s also about an organization working toward a common goal of mutual protection. Keeping everyone involved in safety meetings builds trust that they’ll also be engaged when it counts in a critical event.
- Injury prevention: Even the safest workplace contains hazards to employees’ health and safety. Periodically reviewing risks and how to avoid them can help your team stay safe and healthy.
- Incident review: Discussing accidents, injuries, and even near-misses can help your team learn from mistakes. When you address past incidents, focus on future improvements rather than placing blame to help drive constructive conversation.
- Emergency preparedness: Companies face a variety of emergency scenarios, from natural disasters to equipment failures to civil unrest. Safety meetings are a good time to review preparedness plans and ensure your team knows how to respond.
In most cases, a well-planned safety meeting can fulfill multiple objectives. For example, a meeting on evacuation routes meets OSHA requirements, helps prepare for emergencies, and reduces the likelihood of injuries in the event of a fire or earthquake. It also helps to clarify the employees’ role and responsibility to the organizational culture of safety.
Structure Safety Meetings to Promote Engagement and Knowledge Retention
Think of safety meetings as more than checking a required box. The goal is to keep your team engaged in safety culture and make sure they’re learning. Use these three strategies to develop impactful safety meeting agendas.
Keep meetings short
When you have your whole team together, it can be tempting to cover as much as possible. However, you risk information overload if you go too far at one time. Studies have found average attention spans can range anywhere from 10 to 52 minutes. For most situations, 30-minute safety meetings are ideal. It gives enough time to cover a topic, go over details, and field questions. But it doesn’t drag on long enough to lose people’s attention.
If you expect your planned agenda to run longer—say, an hour or more—try to break it into multiple meetings. For example, if you want to do a deep dive on fire preparedness, hold one meeting about fire prevention and suppression and a separate meeting on equipment shutdown and evacuation.
Provide context and background
With most safety meetings, you’ll have a few key points to communicate. But rather than simply saying them and moving on, explain the hows and whys behind your statements. It might not seem strictly necessary, but expanding on your safety messages increases engagement, which can have a significant impact on retention.
According to Adam Corn, Director of Safety & Security and Training & Development at GoFundMe, employees want to understand the context around information. “People are really interested in the process,” Corn commented. “That’s what adults like to learn. They don’t want to learn just the content. They don’t want to hear, ‘These are the four things I want you to learn today.’ A lot of adults really want to learn the way something’s developed or the process of getting something done, and that is more interesting to an intellectual adult.”
Consider your audience
Every distinct part of your organization engages safety differently. Tailoring meetings accordingly is vital to keeping attendees interested, and there are two components to focus on:
- Technical information and terminology: Describe concepts at a level everyone will understand. Using specialized jargon with people who are unfamiliar will leave them confused and excluded.
- Time sensitivity: Some levels of your organization have greater demands on their time than others, especially executives. Use everyone’s time as efficiently as possible, and avoid fluff or repetition.
Let’s say you’re developing a meeting agenda for construction site safety. If your audience is contractors and hands-on employees, you’d want to cover details of heavy equipment on site and the relevant technical information and safety protocols. But if you’re giving executives a briefing, you could take a higher-level approach, touching on PPE, OSHA compliance, and general safety policies.
7 Components of a Safety Meeting Agenda Template
An effective safety meeting agenda includes these seven sections.
1. Logistical details
All attendees need to have a clear idea of when an where the safety meeting will take place. If you plan the meeting so it’s as easy as possible for everyone involved, you’re establishing the potential for great participation and engagement in critical safety insights.
Every agenda should include these details:
- Location: Where the meeting is taking place, including relevant links and passwords for virtual settings
- Date and time: When people need to be available
- Meeting leader or chairperson: Even if multiple people will be presenting, there should be one point person to field questions or comments before and after the meeting

2. Audience and attendance
Before planning the meeting content, identify who should attend. Depending on the meeting’s purpose, your audience could be anything from a small working group to an entire company. To be respectful of everyone’s time, clarify whether attendance is optional or mandatory. For example, people must attend OSHA-mandated safety training and briefings on new equipment they’ll use. But you might also invite management to participate if they have time, with the understanding their absence won’t derail your plans.
Be sure to take roll call, and after the meeting, review the attendance section of the agenda and see if there were any changes, especially absences. You’ll need to get people up to speed if they missed key information. Tracking attendance is also a good way to optimize planning, as you can ensure safety meetings fit into your teams’ schedules.
3. Meeting topic
For every safety meeting, choose an overarching theme. It can be as broad as “fire preparedness” or as specific as “safe forklift use in rainy conditions.” But it shouldn’t be so ambitious that the meeting’s content feels incomplete.
Meeting themes typically fall into a few categories:
- Monthly safety topics like preparing for winter storms or fire season
- Introduction of new equipment, processes, or safety policies
- Periodic safety committee reviews
- Executive-level safety briefings
- A collection of related short safety talks, such as electrical safety, PPE review, and tool safety at a particular job site
When defining safety meeting agenda topics, try to be as focused as possible. For example, a “workplace safety” topic could encompass an entire company. But you could hold more effective meetings on smaller topics for specific audiences, like ergonomics for office staff and PPE usage for construction or medical staff.
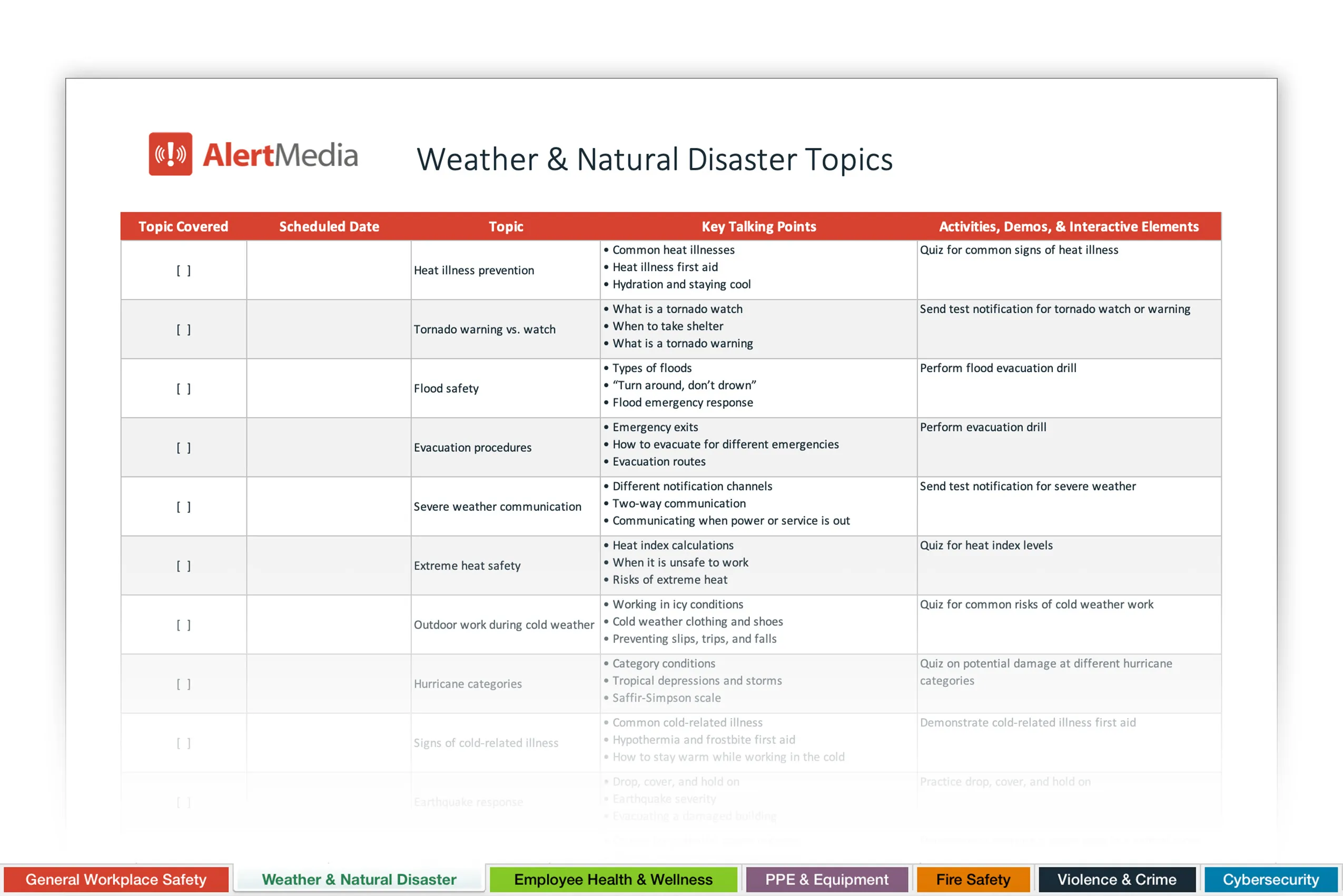
Preview of a spreadsheet full of safety meeting topics and space to fill in your own
4. Previous meeting minutes
It’s a good idea to review notes and ongoing items from the last meeting to make sure things are on track. You may choose to address these items out loud for the entire group, or you may reserve the details for your own records or a small group discussion with safety committee members. You might have good reason to review previous meeting notes during the session if there are action items for people in attendance.
As you develop a safety meeting agenda, it’s the perfect opportunity to review safety meeting minutes and follow-ups to ensure your records are complete and up to date—especially if you have to deal with OSHA audits or safety inspections and reporting in the future.
5. Points of discussion
Within the overarching meeting topic, you’ll have several points to prioritize. The specifics will vary by theme, of course, but this common format is a good place to start:
- An introduction to the purpose and goals of the meeting
- Reports on any recent incidents or injuries
- Ongoing safety issues and corrective actions to takeDetails of new equipment, policies, or procedures
- Safety moments or toolbox talks related to the meeting’s main topic
- Takeaway opportunities to learn more about the topic, such as written documentation or future training programs
- An open discussion for questions, comments, and safety concerns
6. Action items
Most safety meetings will spawn follow-up actions. These relate to the topic of discussion but are outside the scope of the meeting itself. For example, a meeting on earthquake preparedness could lead to action items such as the following:
- Make sure evacuation maps are available throughout your workplace
- Ensure emergency contact lists are current
- Review shutdown procedures for equipment at the facility
- Check emergency supplies like water, food, and first aid kits
- Update templates and protocols for your emergency mass notification platform
Assigning action items achieves two key goals:
- Employees with clear tasks feel engaged and empowered to be a part of the safety process
- Having someone take ownership of responsibilities ensures they don’t fall through the cracks
For each action item, record the pertinent details:
- What the responsibility is
- Who’s responsible for it
- When the deadline is
- Who they should share updates or problems with
And plan to follow up on it at the next safety meeting to share results or feedback with your full team.
7. Plan for the next meeting
Lastly, set up the plan for the next safety meeting. You don’t need to confirm every detail at this point, but it’s good to establish a rough plan:
- Location: This probably won’t change often, but it’s good to confirm that it works for everyone
- Date and time: Collect good times for key attendees so you can lock in a time later
- Proposed topic: What should people expect to cover?
- Meeting leader: A point of contact for needs or questions before the meeting
Use Safety Meetings to Foster a Positive Health and Safety Culture
Safety is an iterative process. Your entire organization needs to remain vigilant, looking for ways to protect themselves and each other. Engaging and informative safety meetings are a key part of that resilient culture.
Sharing information regularly keeps your team current on policies and procedures. And fostering open discussion helps ensure avoidable hazards don’t slip through the cracks. There will always be room to improve your company’s safety, and the next meeting is an opportunity to do just that.